
"Purchase meclizine from india, medicine nobel prize 2015".
By: F. Hamid, M.A., M.D., Ph.D.
Medical Instructor, Indiana Wesleyan University
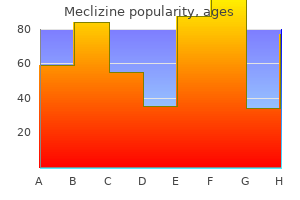
For the tory flow medications similar to lyrica buy meclizine 25mg otc, which is measured using a bubble volume to expand medications on nclex rn order generic meclizine on-line, r must initially pneumotachygraph during FVC measurement medicine nobel prize 2015 buy 25 mg meclizine with mastercard, decrease and ∆P must increase (! As the bubble further expands, r in- distinguishing restrictive lung disease (RLD) creases again (! This model volume, as in pulmonary edema, pneumonia demonstrates that, in the case of two alveoli and impaired lung inflation due to spinal cur- connected with each other (! A4), the smaller vature,whereasOLDischaracterizedbyphysi- one (∆P2 high) would normally become even cal narrowing of the airways, as in asthma, smaller while the larger one (∆P1 low) be- bronchitis, emphysema, and vocal cord paraly- comes larger due to pressure equalization. Surfactantisamixtureof Despopoulos, Color Atlas of Physiology © 2003 Thieme All rights reserved. Surface tension (soap bubble model) r1> r2 ∆P1< ∆P2 ∆P r r1 ∆P r2 ∆P r ∆P1 ∆P2 r 1 2 3 4 B. Maximum breathing capacity (MBC) Maximum respiratory depth and rate +2 Normal +1 Abnormal 0 –1 10s Spirometer Paper feed C. Forced expired volume in first second (FEV1) Maximum expiratory rate +2 +1 Abnormal 0 Normal –1 1s Paper feed 1 Measurement 1. Multiply- O2 diffuses about 1–2µm from alveolus to ing these volumes by the respiratory rate (f in bloodstream (diffusion distance). If,atagiventotalventi- long enough for the blood to equilibrate with lation (VE = VT! When f is doubled and VE T drops to one- blood enters the arterialized blood through. This extra-alveolar shunt as well as ventilation–per- Alveolar gas exchange can therefore decrease fusion inequality (! O2 consumption (VO2) is calculated as the The small pressure difference of about differencebetween. VO2 and VCO2 increase about tenfold cardiacoutput),thecontacttimefallstoathird during strenuous physical work (. Cases B2 and B3 lead to an increase in (100mmHg) and that of CO2 (PACO2) is about functional dead space (! The mean partial pres- B4 lead to inadequate arterialization of the sures in the “venous” blood of the pulmonary blood (alveolar shunt, i. Impairment of alveolar gas exchange Expiration CO2 Inspiration O2 1 Bronchial system Normal alveolar ventilation and perfusion Extra-alveolar shunt From pulmonary artery 4 Non-ventilated alveolus 2 Absent blood flow Alveolar shunt Functional dead space To 3 pulmonary veins Diffusion barrier 121 Despopoulos, Color Atlas of Physiology © 2003 Thieme All rights reserved. In this case, the PAO2 will fluctuate between Ventilation–Perfusion Ratio mixed venous PVO2 and PIO2 of (humidified). B, green line); PAO2 (PACO2) is flowtothelungs,isequaltothecardiacoutput therefore 17. These changes P decreases to about 12mmHg (Pprecap) in the are less pronounced during physical exercise. These values VA/Q imbalance decreases the efficiency of apply to the areas of the lung located at the the lungs for gas exchange. Due to the additive effect of hydrostatic pres- value, the relatively small Q fraction of zone 1. Near the olar–arterial O2 difference (AaDO2) exists (nor- apex of the lung, Pprecap decreases in vessels above mally about 1. Ppostcap), while the sharply, receptors in the alveoli emit local sig- area near the base of the lung (! A, zone 3) is con- nals that trigger constriction of the supplying tinuouslysuppliedwithblood(P.
A linear analog for rating pain with 10- pretreatment buy 25mg meclizine overnight delivery, 15- treatment kidney stones 25mg meclizine fast delivery, and 20-cm lines is significantly less variable than a 5-cm line (5 cm had the largest error symptoms wisdom teeth buy generic meclizine pills, as might have been expected when a 19. Pethidine had no significant effect on the accuracy or reproducibility of the analog rating. Visual analog scales are often used in the belief that the measurement continuum produces greater sensitivity than the discrete points of the categorical scale. Several studies have indicated that there is a clear cor- relation between visual analog scales and categorical scales, but when a visual analog scale alone is used it is unclear what point on the scale represents at least moderate baseline pain intensity. Description of the index The SPADI was developed for use in an outpatient setting. It was de- signed to measure the impact of shoulder pathology in terms of pain and disability, for both current status and change in status over time. The initial version of die SPADI consisted of 20 items grouped into pain and disability subscales, items were selected and placed in either the pain or disability subscale by a panel that included three rheumatol- ogists and a physical therapist. The face validity of each subscale was addressed by selecting items that the panel felt reflected pain and dis- ability associated with shoulder problems. In an effort to improve reliability and validity and to decrease the time required to complete the index, some items were eliminated from each subscale. Items were excluded from the final form of the SPADI if test-retest reliability was low or if correlation with shoulder range of motion on the involved side was low. The pain subscale was reduced from nine to five items and the disability subscale was reduced from 11 to 8 items (Table 21). The SPADI was self-administered and, in its final form, required 5±10 minutes to complete. No pain _____________________ Worst pain imaginable _____ Disability scale How much difficulty do you have? No difficulty _____________________ So difficult Required help _____ Scoring system. Visual analog scales seem to reflect more closely what the subject actually ex- periences and are the most widely employed type of scale in die mea- surement of the pain associated with rheumatic disorders. The visual analog scales used in the SPADI consisted of horizontal lines to which ware attached neither numbers nor divisions. Verbal anchors, represent- ing opposite extremes of the dimension being measured, were placed at either end of the line. The patient was instructed to place a mark on the line in the position that best represented his experience during the past week attributable to the shoulder problem. A numeric score was calculated for each item by arbitrarily dividing the horizontal line into 12 segments of equal length. A number ranging from 0 to 11 was attached to this segment to produce a score for each item. The subscale scores ware calculated by adding the item scores for that subscale and dividing this number by the maximum score possible for the items that were deemed applicable by the subject. Any item marked by the patient as not ap- plicable was not included in the maximum possible score. Therefore, scores could theoretically range from 0 to 100 with higher scores indicating greater impairment.
The combination of more advanced and user-friendly medical image databases is making medical imaging results more accessible to clinical professionals symptoms 2dp5dt cheap meclizine 25 mg visa. Starting in the early 1990s treatment for ringworm order meclizine mastercard, the Visible Human Project and Human Brain Project at the US National Library of Medicine have produced a widely available reference of multimodal images of the human body treatment jokes buy meclizine 25 mg without prescription. These projects provide users with labeled data and the connection of structural- anatomical knowledge with functional-physiological knowledge (Ackerman, 2001; Riva, 2003), and assist in making image data more usable for clinical training and surgery simulation and planning. A significant step in these virtual reality projects is the collection and registration of medical images from multiple imaging modalities. Clinical practice often involves collecting and integrating considerable amounts of multimodality medical imaging data over time intervals to improve the optimization and precision of clinical decision making and to achieve better, faster, and more cost-effective healthcare. For example, in neurosurgical planning, the proper registration of the functional information with the detailed anatomical background enables the surgeon to optimize the operation with minimal damage to the healthy organs. The accurate and efficient registration of the complementary information available from different imaging modalities provides a basis for diagnostic and medical decision-making, treatment monitoring, and healthcare support. A key issue in clinical knowledge management is biomedical image registration, which provides an effective mechanism to integrate the relevant information and knowledge in clinical and medical decision-making, operation planning, and image guided surgery. Registration algorithms also offer new possibilities to analyze and visualize multimodal image datasets simultaneously. Copying or distributing in print or electronic forms without written permission of Idea Group Inc. Positron Emission Tomography (PET) (Courtesy of Hong Kong Sanatorium & Hospital) Using these algorithms, image data from multiple imaging modalities can be matched and presented in a common coordinate system, therefore, anatomical and functional image information can be visualized simultaneously. Hence, biomedical image registration enables clinical professionals a complete insight into the patient data and can help to improve medical diagnosis and patient treatment (Handels, 2003). Applications of biomedical image registration include radiation therapy, interventional radiology, diagnostic and clinical decision-making, image-guided surgery, procedure planning, and simulation, dynamic structural and functional change measurement, treatment, and disease progression monitoring, minimally invasive procedures, and the correlations between the function and morphology of human body. Furthermore, image registration is widely used in biomedical imaging, which includes methods developed for automated image labeling and pathology detection in individuals and groups. Moreover, registration algorithms can encode patterns of anatomic variability in large human populations, and can be used to create disease-specific, population-based atlases (Bankman, 2000). Although biomedical image registration has been intensively investigated and enormous advances in imaging techniques have been achieved, the ever-increasing growth of imaging data and their applications in medical and clinical environments ensures the existence of future challenges in more precise and efficient biomedical image registration. Copying or distributing in print or electronic forms without written permission of Idea Group Inc. Registration of PET image scan with anatomic maps (Courtesy of Hong Kong Sanatorium & Hospital) Background Accurate and efficient biomedical image registration can lead to additional clinical information not apparent in the isolated images and provide clinical professionals with sufficient information for diagnostic and medical decision-making. For example, func- tional imaging such as PET cannot provide very high-resolution image data, but by the registration of these functional images with anatomical images, for example, CT scanning, physiological and functional regions can be located more precisely (Figure 2). After automatic image registration to localize and identify anatomy and lesions, accurate diagnostic and clinical decision-making can be achieved. Such functional-to-anatomical data registration is very useful for clinical diagnosis and surgical operation, especially for telesurgery. By presenting relevant clinical information to clinicians at the point of care, biomedical image registration can improve the quality of care, patient safety, and healthcare benefits. As a fundamental task in image processing, the process of registration aims to match two data sets that may differ in time of acquisition, imaging sensors, or viewpoints. Because of its crucial role in improving healthcare quality, medical image registration has been studied extensively for decades, which has resulted in a bulk of reviews, surveys, and Copyright © 2005, Idea Group Inc. Copying or distributing in print or electronic forms without written permission of Idea Group Inc. Biomedical Image Registration 163 books, for example, Bankman (2000); Brown (1992); Fitzpatrick, Hill, and Maurer (2000); Lester and Arridge (1999); Maintz and Viergever (1998); Mäkelä (2002); Maurer and Fitzpatrick (1993); Rohr (2000); and van den Elsen, Pol, and Viergever (1993),. According to the registration feature space, principally, medical image registration can be distin- guished into intensity-based registration and feature-based registration (Brown, 1992).
If these genes have changes within them treatment restless leg syndrome buy genuine meclizine online, the instructions “Oto Palato Digital Syndrome Type I and II treatment quadratus lumborum purchase discount meclizine on-line. Therefore medicine while breastfeeding order meclizine on line, all ovarian cancers are genetic because they all result from changes within genes. Johnson is that most ovarian cancers are caused by sporadic changes within the genes, and only a minority are caused by inherited genetic alterations. A small proportion of ovarian cancer is caused by Ovarian cancer is a disease in which the cells in the inherited genetic alterations. As of 2001, a genetic alter- ovaries become abnormal and start to grow uncontrol- ation causing a predisposition solely to ovarian cancer lably, forming tumors. However, in 1994 a breast and cers develop in the cells that line the surface of the ovarian cancer susceptibility gene, known as BRCA1 ovaries and are called “epithelial cell tumors. Description Women with alterations in these genes have an increased The ovaries are a pair of almond-shaped organs that risk for breast and ovarian cancer, and men have an lie in the pelvis on either side of the uterus. In addition, they also produce the (in men and women) are also associated with BRCA2 female hormones estrogen and progesterone, which reg- alterations. Nearly all individuals with BRCA alterations difficult to discover in the early stages. This is often have a family history of the alteration, usually a parent because there are no obvious warning signs, and the dis- with it. In turn, they also may have a very strong family ease can grow relatively quickly. In addition, the ovaries history of breast, ovarian, prostate, colon, and/or pancre- are situated deep in the abdomen and small tumors may atic cancers. Aside from BRCA1 and BRCA2, there 866 GALE ENCYCLOPEDIA OF GENETIC DISORDERS likely are other cancer susceptibility genes that are still unknown. KEY TERMS In addition to BRCA1 and BRCA2, ovarian cancer may be present in rare genetic cancer syndromes. In these Alteration—Change or mutation in a gene, specif- instances, an individual may have other health problems ically in the DNA that codes for the gene. As an example, Hereditary examination of living tissue for diagnostic pur- Non-Polyposis Colorectal Cancer (HNPCC) is a syn- poses. HNPCC is due to changes in sev- procedure that produces a three-dimensional pic- eral genes including hMLH1, hMSH2, hMSH6, and ture of organs or structures inside the body, such as hPMS2. Laparoscopy—A diagnostic procedure in which a Demographics small incision is made in the abdomen and a slen- der, hollow, lighted instrument is passed through On average, a North American woman faces a life- it. The doctor can view the ovaries more closely time risk of approximately 2% to develop ovarian cancer. The American Cancer Society states Laparotomy—An operation in which the abdomi- that in the year 2000 about 23,100 new cases of ovarian nal cavity is opened up. Specific BRCA alter- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)—A technique ations are common in certain ethnic groups, which may that employs magnetic fields and radio waves to make hereditary ovarian cancer more common in these create detailed images of internal body structures populations. Ovarian cancer has no specific signs or symptoms in Transvaginal ultrasound—A way to view the the early stages of the disease. A probe is inserted rience some of the following: into the vagina and the ovaries can be seen. Color doppler imaging measures the amount of blood • Pain or swelling in the abdominal area flow, as tumors sometimes have high levels of • Bloating and general feeling of abdominal discomfort blood flow. This • Close genetic relationships between people with cancer, is why it is important for a physician to be informed right such as parent-child, sibling-sibling away if any of the above symptoms are present.
PELVIC EXAMINATION Indications • Part of a complete physical examination in the female • Used to assist in the diagnosis of diseases and conditions of the female genital tract Materials • Gloves • Vaginal speculum and lubricant • Slides symptoms 9 dpo quality 25mg meclizine, fixative (Pap aerosol spray medications an 627 purchase meclizine online pills, etc) symptoms of a stranger 25mg meclizine visa, cotton swabs, endocervical brush and cervi- cal spatula prepared for a Pap smear • Materials for other diagnostic tests: Culture media to test for gonorrhea, Chlamy- 13 dia, herpes; sterile cotton swabs, plain glass slides, KOH, and normal saline solu- tions, as needed Procedure 1. The pelvic exam should be carried out in a comfortable fashion for both the patient and physician. The patient should be draped appropriately with her feet placed in the stirrups on the examining table. Pre- pare a low stool, a good light source, and all needed supplies before the exam begins. In unusual situations examinations are conducted on a stretcher or bed; raise the pa- tients buttocks on one or two pillows to elevate the perineum off the mattress. Observe the skin of the perineum for swelling, ulcers, condylomata (venereal warts), or color changes. Inspect the vaginal orifice for discharge, or protrusion of the walls (cystocele, rec- tocele, urethral prolapse). Use a speculum moistened with warm water not with lubricant (lubricant will in- terfere with Pap tests and slide studies). Because the anterior wall of the vagina is close to the urethra and bladder, do not exert pressure in this area. With the speculum directed at a 45-degree angle to the floor, spread the labia and insert the speculum fully, pressing posteriorly. Inspect the cervix and vagina for color, lacerations, growths, nabothian cysts, and evidence of atrophy. Inspect the vagina for secretions and obtain specimens for a Pap smear, other smear, or culture (see tests for vaginal infections and Pap smear in item 7). Inspect the vaginal wall; rotate the speculum as you draw it out to see the entire canal. It is best to use whichever hand is comfortable to do the in- ternal vaginal exam. Place lubricant on the first and second gloved fingers, and then, keeping pressure on the posterior fornix, introduce them into the vagina. Place the examining fingers on the posterior wall of the vagina to further open the introitus. Note the size, shape, consistency, and motility, and test for ten- derness (the so-called chandelier sign or marked cervical tenderness, which is positive in PID). With your fingers in the vagina posterior to the cervix and your hand on the ab- domen placed just above the symphysis, force the corpus of the uterus between the two examining hands. Move the fingers in the vagina to one or the other fornix, and place the hand on the abdomen in a more lateral position to bring the adnexal areas under examination. Insert your index finger into the vagina, and place the well-lubricated middle fin- ger in the rectum. Palpate the posterior surface of the uterus and the broad ligament for nodularity, tenderness, or other masses. It may also be helpful to do a test for occult blood if a stool specimen is available. Papanicolaou (Pap) smear: The Pap smear is helpful in the early detection of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and carcinoma. It is recommended that low-risk patients have routine Pap smears done every 2–3 y, but only after three annual Pap smears are negative. With the unlubricated speculum in place, use a wooden cervical spatula to obtain a scraping from the squamocolumnar junction.
Buy meclizine australia. Top 10 Terrible Things Smoking Does to Your Body.