
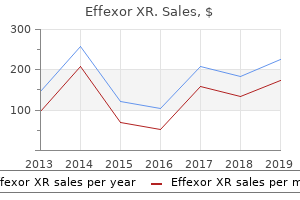
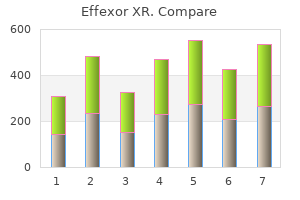
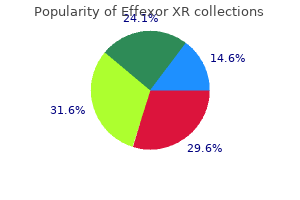
"Order 37.5mg effexor xr amex, anxiety symptoms preschooler".
By: S. Yorik, M.B. B.CH. B.A.O., M.B.B.Ch., Ph.D.
Professor, University of Tennessee College of Medicine
These harder anxiety 8 months postpartum generic effexor xr 75mg otc, transparent the nakedness of our skin does lead to some problems anxiety symptoms of menopause order online effexor xr. Skin cancer cells are then pushed forward over the strata basale and spinosum occurs frequently in humans anxiety symptoms restless legs discount 37.5 mg effexor xr overnight delivery, particularly in regions of the skin ex- posed to the sun. Fingernails grow at the rate of approximately related to the fact that hair is not present to dissipate the oily secre- 1 mm each week. The condition of nails may be indicative of a person’s general health and well-being. Nails should appear pinkish, showing the rich vascular capillaries beneath the translucent nail. A yellowish Nails hue may indicate certain glandular dysfunctions or nutritional defi- ciencies. A The nails on the ends of the fingers and toes are formed from the prominent bluish tint may indicate improper oxygenation of the blood. The Spoon nails (concave body) may be the result of iron-deficiency ane- hardness of the nail is due to the dense keratin fibrils running par- mia, and clubbing at the base of the nail may be caused by lung cancer. Dirty or ragged nails may indicate poor personal hygiene, allel between the cells. Both fingernails and toenails protect the and chewed nails may suggest emotional problems. Each nail consists of a body, free border, and hidden bor- Glands der (fig. The platelike body of the nail rests on a nail bed, which is actually the stratum spinosum of the epidermis. The Although they originate in the epidermal layer, all of the glands body and nail bed appear pinkish because of the underlying vas- of the skin are located in the dermis, where they are physically cular tissue. The sides of the nail body are protected by a nail supported and receive nutrients. Integumentary System © The McGraw−Hill Anatomy, Sixth Edition Companies, 2001 118 Unit 4 Support and Movement Sebaceous gland Sweat gland FIGURE 5. The coiled structure of the ductule portion of the gland (see ar- rows) accounts for its discontinuous appearance. If the ducts of sebaceous glands become blocked for some reason, the glands may become infected, result- ing in acne. Sex hormones regulate the production and secretion of sebum, and hyperactivity of sebaceous glands can result in se- rious acne problems, particularly during teenage years. Sudoriferous Glands Eccrine Commonly called sweat glands, sudoriferous glands excrete per- Apocrine sweat gland spiration, or sweat, onto the surface of the skin. Perspiration is sweat gland composed of water, salts, urea, and uric acid. It serves not only for evaporative cooling, but also for the excretion of certain FIGURE 5. Sweat glands are most numerous on the palms, soles, axil- lary and pubic regions, and on the forehead. They are coiled and to as exocrine, because they are externally secreting glands that tubular (fig. These glands are formed before birth and function in evap- Sebaceous Glands orative cooling (figs. Apocrine sweat glands are much larger than the eccrine with hair follicles, because they develop from the follicular ep- glands. They are holocrine glands (see chapter 4) where they secrete into hair follicles.
There are a few exceptions to this rule: some sympathetic neu- Objective 8 List the neurotransmitters of the preganglionic rons that innervate blood vessels in skeletal muscles anxiety symptoms breathing problems generic 37.5 mg effexor xr free shipping, as well as and postganglionic neurons of the sympathetic and sympathetic neurons to sweat glands i have anxiety symptoms 247 order effexor xr 150mg with visa, release acetylcholine (are parasympathetic divisions anxiety counseling buy effexor xr with a mastercard. Acetylcholine is also the transmitter released by all Objective 10 Explain the antagonistic, complementary, and parasympathetic postganglionic neurons at their synapses with cooperative effects of sympathetic and parasympathetic effector cells (fig. In other words, a cholinergic fiber is a neuron that secretes ACh at the terminal end of its axon. Mass acti- vation of the sympathetic division prepares the body for intense Responses to Adrenergic Stimulation physical activity in emergencies; the heart rate increases, blood glucose rises, and blood is diverted to the skeletal muscles (away Adrenergic stimulation—by epinephrine in the blood and by nor- from the visceral organs and skin). These and other effects are epinephrine released from sympathetic nerve endings—has both listed in table 13. The theme of the sympathetic division is excitatory and inhibitory effects. The heart, dilatory muscles of aptly summarized in the phrase fight or flight. The smooth muscles of the bronchioles and of many ways opposite to the effects of sympathetic stimulation. The some blood vessels, however, are inhibited from contracting; parasympathetic division, however, is not normally activated as a adrenergic chemicals, therefore, cause these structures to dilate. Stimulation of separate parasympathetic nerves can result in slowing of the heart, dilation of visceral blood vessels, and in- creased activity of the GI tract (table 13. Autonomic Nervous © The McGraw−Hill Anatomy, Sixth Edition Coordination System Companies, 2001 Chapter 13 Autonomic Nervous System 445 TABLE 13. This drug, however, does not affect the cholinergic receptors of skele- Somatic motor neurons, postganglionic parasympathetic neu- tal muscle or those of autonomic ganglia. The acetylcholine re- rons, and all preganglionic autonomic neurons are cholinergic— ceptors of visceral organs are therefore said to be muscarinic. The cholinergic effects of somatic motor neurons and preganglionic autonomic The muscarinic effects of ACh are specifically inhibited by the drug atropine, derived from the deadly nightshade plant neurons are always excitatory. Indeed, extracts of this plant were used glionic parasympathetic neurons are usually excitatory, with by women during the Middle Ages to dilate their pupils (at- some notable exceptions; the parasympathetic neurons innervat- ropine inhibits parasympathetic stimulation of the iris). Autonomic Nervous © The McGraw−Hill Anatomy, Sixth Edition Coordination System Companies, 2001 446 Unit 5 Integration and Coordination Central Nervous System Cranial Terminal parasympathetic ganglion nerves Visceral ⊃• ACh ACh effectors Paravertebral ganglion ⊃• NE Visceral ACh effectors Adrenal medulla Sympathetic ACh E, NE (hormones) (thoracolumbar) nerves ⊃ • NE Visceral ACh effectors Collateral ganglion Sacral parasympathetic Visceral nerves ⊃ • effector ACh ACh organs FIGURE 13. Those nerves that release ACh are called cholinergic; those that release NE are called adrenergic. The adrenal medulla secretes both epinephrine (85%) and norepinephrine (15%) as hormones into the blood. Organs with Dual Innervation which is stimulated by impulses through sympathetic nerve end- ings, causes dilation; contraction of the pupillary constrictor Many organs receive dual innervation—they are innervated by muscle, which is innervated by parasympathetic nerve endings, both sympathetic and parasympathetic neurons. Complementary Effects The effects of sympathetic and parasympathetic stimulation on Antagonistic Effects salivary gland secretion are complementary. The secretion of wa- The effects of sympathetic and parasympathetic innervation on tery saliva is stimulated by impulses through parasympathetic the sinoatrial (SA) node (“pacemaker”) of the heart (see fig. In this case, sympathetic and parasympathetic neurons in- stimulate the constriction of blood vessels throughout the GI nervate the SA node. The resultant decrease in blood flow to the salivary glands neurons increases the heart rate, whereas cholinergic stimulation causes the production of a thicker, more viscous saliva. Antagonism is also seen in the GI tract, where sympathetic nerves inhibit and parasympathetic nerves Cooperative Effects stimulate intestinal movements and secretions. The effects of sympathetic and parasympathetic stimulation on the The effects of sympathetic and parasympathetic stimula- urinary and reproductive systems are cooperative. Erection of the tion on the diameter of the pupil of the eye are analogous to the penis, for example, is due to vasodilation resulting from action po- reciprocal innervation of flexor and extensor skeletal muscles by tentials through parasympathetic nerves; ejaculation is due to action somatic motor neurons. This is because the iris contains antago- potentials through sympathetic nerves.
Filtering a small volume (fluid permeability) and surface area of the glomerular filtra- out of the glomerular capillary would lead to a sharp rise tion barrier anxiety reduction buy cheap effexor xr on line. In chronic renal disease anxiety yeast infection cost of effexor xr, functioning glomeruli in COP early along the length of the glomerulus anxiety upper back pain buy effexor xr 75mg amex. As a are lost, leading to a reduction in surface area available for fil- consequence, filtration would soon cease and GFR would tration and a fall in GFR. On the other hand, a high blood flow would al- mones appear to change glomerular Kf and, thus, alter GFR, low a high rate of filtrate formation with a minimal rise in but the mechanisms are not completely understood. In general, renal blood flow and GFR change hand in hand, but the exact relation between GFR and renal Glomerular Capillary Hydrostatic Pressure. Glomerular blood flow depends on the magnitude of the other fac- capillary hydrostatic pressure (PGC) is the driving force for tors that affect GFR. Be- cause of autoregulation, P and GFR are maintained at rel- Several Factors Contribute to the High GFR GC atively constant values when arterial blood pressure is var- in the Human Kidney ied from 80 to 180 mm Hg. Below a pressure of 80 mm Hg, The rate of plasma ultrafiltration in the kidney glomeruli however, PGCand GFR decrease, and GFR ceases at a blood (180 L/day) far exceeds that in all other capillary beds, for pressure of about 40 to 50 mm Hg. One of the classic signs several reasons: of hemorrhagic or cardiogenic shock is an absence of urine 1) The filtration coefficient is unusually high in the output, which is due to an inadequate PGC and GFR. Compared with most other capillaries, the The caliber of afferent and efferent arterioles can be glomerular capillaries behave as though they had more altered by a variety of hormones and by sympathetic pores per unit surface area; consequently, they have an un- nerve stimulation, leading to changes in PGC, glomerular usually high hydraulic conductivity. Some hormones act preferentially 2 filtration barrier area is large, about 2 m. Afferent arteriolar dila- 2) Capillary hydrostatic pressure is higher in the tion increases glomerular blood flow and PGC and, there- glomeruli than in any other capillaries. Afferent arteriolar 3) The high rate of renal blood flow helps sustain a high constriction produces the exact opposite effects. Efferent GFR by limiting the rise in colloid osmotic pressure, favoring arteriolar dilation increases glomerular blood flow but filtration along the entire length of the glomerular capillaries. Constric- In summary, glomerular filtration is high because the tion of efferent arterioles increases PGC and decreases glomerular capillary blood is exposed to a large porous sur- glomerular blood flow. With modest efferent arteriolar face and there is a high transmural pressure gradient. With extreme efferent arteriolar constriction, however, TRANSPORT IN THE PROXIMAL TUBULE GFR decreases because of the marked decrease in glomerular blood flow. Glomerular filtration is a rather nonselective process, since both useful and waste substances are filtered. By contrast, tubular transport is selective; different substances are trans- Hydrostatic Pressure in Bowman’s Capsule. Some substances are reab- tic pressure in Bowman’s capsule (PBS) depends on the input sorbed, others are secreted, and still others are both reab- of glomerular filtrate and the rate of removal of this fluid by sorbed and secreted. It also provides urine depends in large measure on the magnitude of tubu- the driving force for fluid movement down the tubule lu- lar transport. If there is obstruction anywhere along the urinary in the various nephron segments. Here we describe trans- tract—for example, stones, ureteral obstruction, or prostate port along the nephron and collecting duct system, starting enlargement—then pressure upstream to the block is in- with the proximal convoluted tubule. If tubular reabsorp- The proximal convoluted tubule comprises the first 60% tion of water is inhibited, pressure in the tubular system is of the length of the proximal tubule. Because the proximal increased because an increased pressure head is needed to straight tubule is inaccessible to study in vivo, most quanti- force a large volume flow through the loops of Henle and tative information about function in the living animal is collecting ducts. Consequently, a large increase in urine confined to the convoluted portion.
The teeth most commonly injured during anesthesia are the two upper front incisors (numbers 8 and 9) severe anxiety symptoms 247 buy generic effexor xr 37.5 mg, which are vulnerable to laryngoscope pres- sure during visualization of the vocal cords and to pressure from a Chapter 10 / Anesthesiology 125 semi-awake patient biting down directly on a hard substance anxiety symptoms upper back pain generic effexor xr 150mg on-line. These upper teeth may be bonded or capped for cosmetic reasons anxiety facts generic effexor xr 75 mg without a prescription, making them even more vulnerable to damage. Prosthetic dental work, like permanent bridges, also seem particularly vulnerable to problems dur- ing airway management. Anesthesiologists are encouraged to specifically inquire about pre- existing dental work, especially in the front of the mouth. If invasive airway management (such as endotracheal tube or LMA placement) is planned, anything that is usually removable by the patient should be taken out of the mouth in advance. Anesthesiologists are also encour- aged to specifically examine their patients’ teeth preoperatively, mak- ing written notations regarding pre-existing damage, especially to the front teeth. Chipped, broken, or loose teeth can be pointed out to the patient, who may not even be aware that such damage already exists. If vulnerable teeth are noted, the anesthesiologist can consider using plastic oral dental guards or gauze packs placed in the sides of the mouth to prevent voluntary occlusion. Oral airways can be removed or exchanged for nasal airways during recovery before a patient is awake enough to bite down forcibly. Informed consents for general anesthesia should mention dental injury because it is so common and because patients who have been forewarned about this possibility are less likely to be angry and liti- gious should it actually occur. In the event of accidental dental injury, an anesthesiologist should be frank and honest with the patient about what has happened. In actuality, dental injury is within the risks of anesthesia, but anesthesiologists often become defensive, arguing, “It’s not my fault, I didn’t do anything wrong. Frequently, dental claims are settled by reimbursing the patient for the cost of repairing the teeth to their pre-anesthesia state. To avoid inflated estimates, an evaluation by an independent dentist, who will not actually be doing the repairs, is often sought. Anesthesiologists are advised to first try working with patients directly to get these situa- tions resolved in a way that seems fair and equitable to everyone. Occasionally a dental claim does escalate, with the patient and anes- thesiologist generating legal bills many times greater than the cost of the actual dental repairs. Any physician who reimburses a patient directly is advised to obtain a liability release from that patient accept- ing that as payment in full (2). These are cases in which anesthesia errors directly cause serious patient injuries, including brain damage or death. In an era of sophisticated anesthetic techniques and monitoring, it is easy to forget that cases like these still can and do occur. Peer review of these claims has led to a series of risk management suggestions. MONITORING Since the widespread adoption of the pulse oximeter and end-tidal CO2 monitors, anesthesia has become much safer. However, serious injuries still result because of failures to use the monitors correctly. Inactivation of the pulse oximeter alarm accounts for a large propor- tion of anoxic injury cases that involve respiratory insufficiency that is noticed too late. Anoxic damage can occur within minutes of an unrecognized and untreated respiratory arrest, even in an operating room. Anesthesiologists should be very careful when silencing the auditory alarms on these monitors, especially if they are not positive they will remain directly in their line of sight. It is also important to remain vigilant with sedated patients having MAC or regional blocks, as the level of sedation can often deepen without warning.
Order effexor xr 75mg online. Marvel Comics Review: Absolute Carnage: Separation Anxiety.